Commonly used oxidants are chlorine, bleach solution or slurry, sodium hypochlorite solution, and the like. It is the most effective way to destroy cyanide. When chlorine is used as the oxidant, the base should be added at the same time. The chlorination method generally uses bleaching powder (CaOCl 2 ) as an oxidizing agent, but the addition of the bleaching powder generates a large amount of sludge, and the labor for cleaning the slag is large. Although chlorine or sodium hypochlorite is used, the amount of slag is small, and the operation is convenient, but it is unsafe and produces a heavy irritating odor. The base used may be sodium hydroxide or lime milk. The chlorination method is usually carried out under the conditions of pH 8. 5 to 11 (generally 9). When the pH is above 11, cyanate is easily oxidized by chlorine (less than 1 min) to complete the reaction to form CNO - ions: CN - +Cl 2 +2OH - CN - +OCl - Since the oxidation process is sufficient to produce CNO - ion in solution after only a thousandth of residual CN -. When the above reaction occurs at a pH of less than 8.5, a toxic CNCl gas is evolved and the reaction rate is slowed down. CNO - ions should be further decomposed under control conditions of pH8 ~ 8.5. The decomposition reaction at this time is slower than the previous reaction, and usually takes more than 0.5h to complete: 2CNO+3Cl 2 +4OH - 2CNO - +3OCl - +H 2 O - The amount of chlorine required for the free cyanate oxidation process is almost equal to the stoichiometric amount, but different methods produce different cyanides. In addition, since many other oxidizable substances (such as S 2 O 3 2 - and CNS - ) are present in the cyanide solution, and in order to make the reaction more sufficient, the solution should contain a certain amount of residual chlorine, so the actual chlorine The consumption is greater than the amount of chlorine required to oxidize cyanide. The theoretical amount (mass ratio) of the oxidizing agent and the base calculated from the reaction formula is shown in the following table. The chlorine in the table below is active oxygen. In calculation, liquid chlorine is calculated according to 100% chlorine, bleaching powder containing 20% ​​to 30% chlorine, and sodium hypochlorite containing 10% chlorine. Table The ratio of the theoretical amount of oxidant and base to the mass ratio of cyanate Cyanate Cyanate generation stage Final oxidation stage chlorine Sodium oxychloride Calcium oxide chlorine Sodium hydroxide Calcium oxide 1 2.73 3.10 2.15 6.83 6.20 4.31 It can be seen from the above table that by using the chlorination oxidation method, theoretically removing a portion of cyanide requires consumption of 6.83 parts of chlorine. However, in actual operation, due to the large amount of waste thiocyanate, sulphide, the reduced state metal ions and their compounds, and chlorine and disproportionation in order to ensure that there is sufficient residual waste such as chlorine, chlorine often actually consumed Up to 1:15. The cyanide-containing cyanide-containing waste liquid is usually treated by a batch process. This treatment method is easier to adapt to changes in water volume and cyanide concentration, and can achieve the desired treatment effect safely and reliably. When the amount of waste liquid is too large, continuous treatment is often used to reduce equipment and floor space. However, continuous treatment often does not effectively control the concentration of cyanide in the effluent. The equipment system for purifying cyanide-containing sewage with chlorine gas in a sealed reaction tank of a factory in China is shown in Fig. 1. Figure 1 Equipment system for chlorine-containing purification of cyanide-containing sewage 1-chloro gas cylinder; 2-chlorination machine; 3- ejector; 4-mixing tank; 5- pump house; 6-rotor flowmeter; 7-reaction tank The practice of the chlorination oxidation method proves that in order to control the concentration of cyanide in the effluent to be less than 0.05 mg ∕L, it is necessary to maintain 3 to 5 mg of residual active chlorine in the treated waste liquid. However, in view of their toxic chlorine, thiosulfate must be added before discharge to the waste liquid, with ferrous sulfate or ammonium sulfate which was removed. When chlorine is removed by ferrous sulfate, the amount of ferrous sulfate can be added in a weight ratio of Cl:FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O = 1:32: 3Cl 2 +6FeSO 4 In view of the bactericidal action of chlorine, such as the discharge of residual chlorine solution directly into the urban sewer, it is not necessary to remove chlorine. A mine uses an alkaline chlorination method with bleaching powder to treat a tailings slurry with a pH of about 10 and a CN - average of 150 mg ∕L. Press pulp CN - 1:9 ~ 10 reaction ratio of bleach to a septic tank 1h, which may be simple cyanide (CN -) and not very stable complex cyanide [Zn (CN) 4 2 -, etc.] It is completely destroyed and can make the extremely toxic highly stable cyano complex [Fe(CN) 6 3 - , Fe(CN) 6 4 - etc.) practically non-toxic. When the tailings slurry contains CN - 159mg ∕L, the amount of bleaching powder is 2.5kg / t, and the purified clarified water containing CN - can be reduced to 0.04mg ∕L.
As a single sided PCB manufacturer, Jinghongyi PCB has been single sided PCB for many years. Production and manufacturing experience, with a very exquisite single sided PCB manufacturing process flow chart.
Basically, there is no challenge for PCB manufacturer to produce single sided PCB and the technology is quite mature nowadays. The main focus for PCB manufacturer is how to control production cost and save more cost for customers.
It is the type of a single layer PCB which is made up a rigid material such as fiber glass. These PCBs are inflexible and prevent the circuit from bending and breaking. Currently these are used in different types of devices such as in calculators and power supplies etc.
It is the type of a single layer PCB which is mode out a flexible material instead of a rigid material and for this purpose plastic materials are used. It has so many advantages over single layer rigid pub but it fabrication cost is so much high.
It is the type of a single layer PCBs which is used for high frequency circuits normally in giga hertz. These PCBs are made out a Teflon or polyphenylene oxide (PPO) material. During choosing high frequency single layer PCB many aspects are keep in mind such as dielectric loss, thermal expansion and water absorption etc.
It the type of single layer PCBs which is made out by the combination of plastic and fiber glass. Both materials are combined together into single layer. It has so many advantages over single layer rigid and flexible PCB such as it reduces the weight and size of overall PCB.
single sided vs double sided PCB
Single Sided PCB, Single Layer PCB, 1 Layer PCB, making circuit boards JingHongYi PCB (HK) Co., Limited , https://www.pcbjhy.com![]() CNO - +2Cl - +H 2 O
CNO - +2Cl - +H 2 O ![]() CNO - +Cl -
CNO - +Cl - ![]() 2CO 2 ↑+N 2 ↑+6Cl - +2H 2 O
2CO 2 ↑+N 2 ↑+6Cl - +2H 2 O ![]() 2CO 2 ↑+N 2 ↑+3Cl - +2OH -
2CO 2 ↑+N 2 ↑+3Cl - +2OH - 
![]() 2Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 +2FeCl 3
2Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 +2FeCl 3
The Single Most Important Thing You Need To Know About SINGLE SIDED PCB
We can produce single-sided copper PCB, single sided copper clad PCB board, single sided flex PCB.
We know that when you choose single sided PCB manufacturer, product quality is one of the first factors you need to consider. We are not only engaged in PCB manufacturing for many years, but also one of the large-scale PCB manufacturers in China. We can not only produce single sided PCB, but also double-sided PCB, Multilayer PCB , Aluminum PCB and so on.
In addition to product quality, you may also need to consider the single sided PCB price factor. If you choose us as your partner, you can rest assured that we will be able to provide you with not the best price on the premise of guaranteeing product quality, but the price that we both feel is very reasonable. What do you think?
In this article, we will elaborate on the definition, type, cost components, structure, advantages and disadvantages, manufacturing process and raw materials of single sided PCB. Finally, we will introduce the application of single sided PCB and the differences between single sided PCB and Double Sided PCB. And how to choose between single sided PCB and double sided PCB.
What Is Single Sided PCB

Single-sided PCB diagram mainly used Network Printing(Screen Printing), that is, resist on copper surface, After etching, mark the welding resistance, and then finish the hole and the shape of the part by punching.
Fundamentally, single-sided and double-sided printed circuit boards serve the same purpose. Both serve as catalysts for electrical connections between components, however there are some key differences that set them apart from each other. More specifically, they differ in the costs associated with production and development processes, as well as ampacity differences.
With the appearance of electronic transistor, single sided PCB was developed in the early of 1950, which is mainly manufactured in USA. Single-sided PCB was manufactured by copper etching directly at that time. During 1953 to 1955, Japan use imported copper make out paper phenolic aldehyde copper substrate, and apply mainly on radio products. In 1956, single-sided PCB technology was made big progress with the appearance of professional PCB manufacturers from Japan. In the early stage, copper substrate mainly used paper phenolic aldehyde, but because paper phenolic aldehyde with the factors of low electric insulation, bad solder thermal stability, twist issue etc, paper epoxide resin and glass fiber epoxy resin was developed soon after. Currently, paper epoxide resin is widely used in consuming electronic.
Types of Single Layer PCB
It the type of single layer PCB which is made out with aluminum material substrate. The design of this PCB is almost same as copper backed PCB but only difference is that, in these PCBs aluminum substrate is used instead of copper. Aluminum backed is used with thermal insulating material for transferring the heat from insulating material to back.
What Goes Into Determining single sided PCB Costs and price
No matter whether manufacturing a single-sided PCB, double-sided PCB, or multilayer PCB, three main cost categories exist: Primary production costs, dependent costs, and overhead costs.
Often, single layer PCB are used for simple devices and usually cheaper than multilayer PCB.
Multilayer PCB has one or multiple conductor patterns inside the board, this increases the area available for wiring. multilayer PCB, such as 4 Layer PCB , 6 Layer PCB and 8 Layer PCB are usually used for more complicated devices. For example, smart phones use 12 layers due to the various demands of the circuit. As a result, multilayer PCB circuit boards are more expensive.
You can break them down into the following categories:
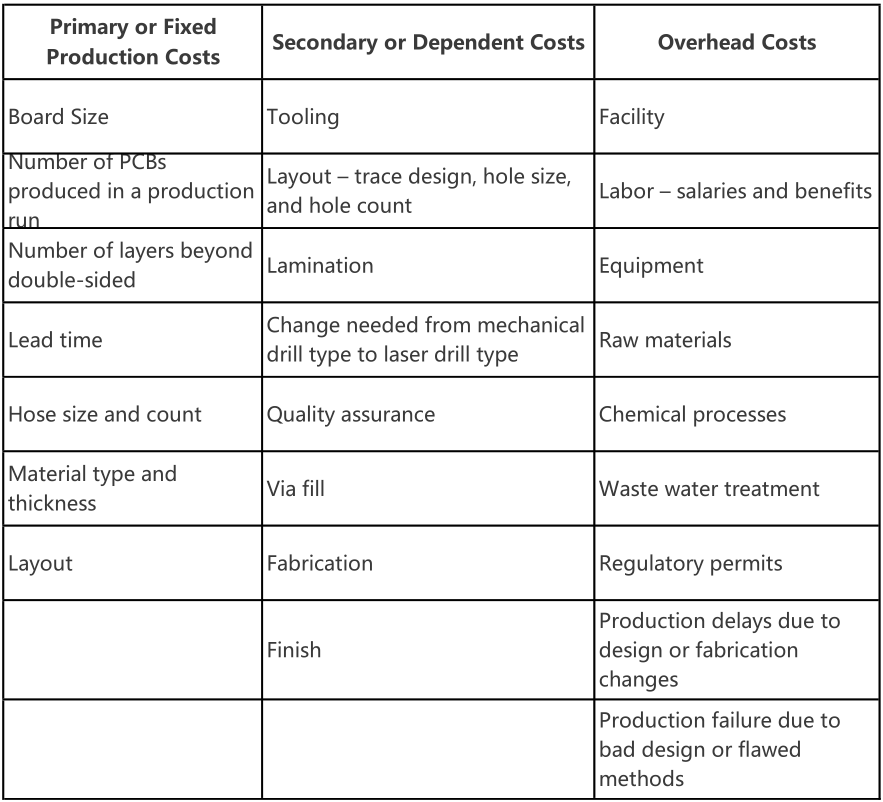
Layout alters the cost balance. While the number and size of holes remain the same with single-sided PCBs, two different circuit designs on one substrate change the number of holes and add vias.
Because double-sided PCBs welcome complex circuit designs, layout also becomes a dependent factor. As the number of traces increase, costs increase. Smaller surface mount components fastened to the bottom side change the trace spacing. As the space between the traces narrows, costs can jump 5 to 10 percent.
Different layouts may require different hole sizes and the use of laser rather than mechanical drills. Smaller hole sizes and larger hole counts drive the cost higher because of a change in the manufacturing process.
Advantages of Single Sided PCB

Single Layer PCB Disadvantages
Despite their cost advantages and other perks, single-layer boards are not the right choice for every project due to the limitations they have, which include:
How to make single sided PCB

Single sided PCB manufacturing Process flow chart
One thin layer of thermally conductive but electrically insulating dielectric is laminated with copper. Soldermask is usually applied on top of the copper.
Cutting - Cleaning - Drilling - Cleaning - PTH - Panel - Plating - Cleaning - Photolithography - Image Transfer - Inspection - Copper/Tin - Plating - Coating - Removing/Etching/Tin - Removing - Inspection - Cleaning - Solder - Mask - Exposure/Develop/Inspection - Prepreg - Screen - HASL - Conformal - Coating - Post - Soldering - Cleaning - Test - Final Inspection - Packing
Single layer PCB Raw Material
Construction of Single Sided PCB
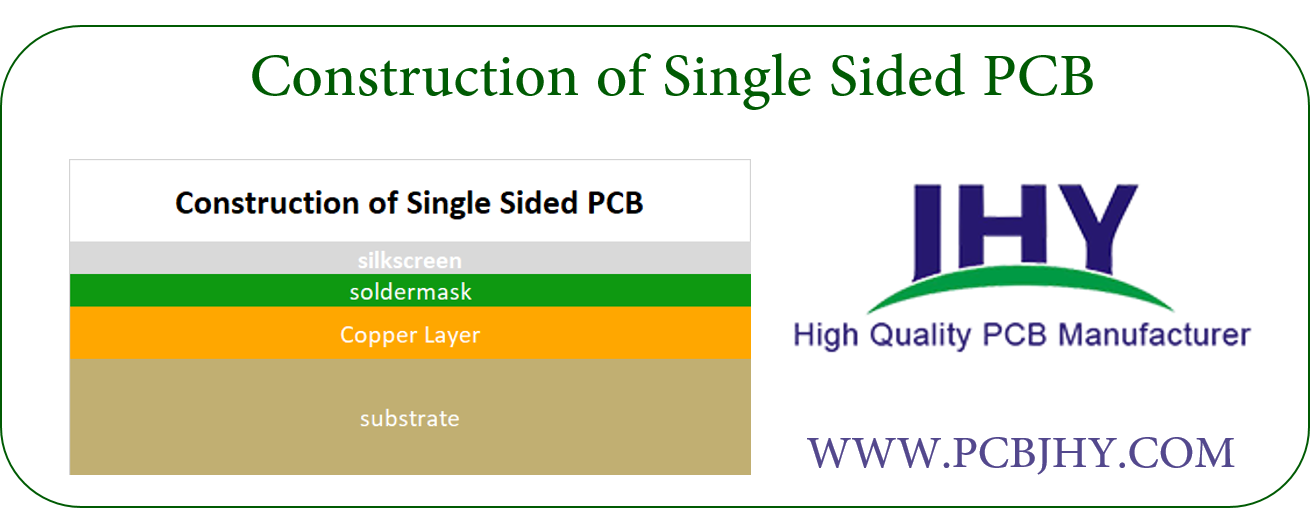
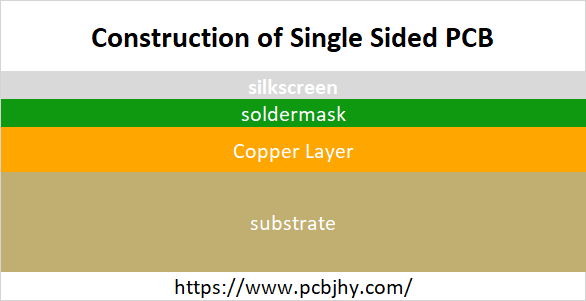
The base material, which is also named as substrate, is composed of insulating fiber glass which gives PCB strength and compact look. The nature and type of base material defines if board is going to be Flexible PCB or Rigid PCB.
Above substrate, there lies a copper layer which provides conducting path for various components on the board. The copper thickness is different for different boards depending on your needs and requirements and is defined in ounces per square foot.
On the top of copper foil, there exists a solder mask layer. This layer is mainly used for protection and makes the copper foil insulating which helps in avoiding the conduction in case direct contact happens with some conducting material.
On the top of all layers, there exists a silkscreen layer that is mainly used for adding symbols and characters on the board so a common person can anticipate the clear understanding of the board.
Single-Sided PCB Applications
What Is Double-Sided PCB
It need circuits on both sides. Via is the holes on boards, coated with metal and it can connect wires on both sides. Because the area of Double-sided PCB is twice as large as the Single-sided PCB, and because the wiring is interleaved, which is better suited for circuits that are more complex.
Someone may feel confused that if one Double-sided PCB, wires on both sides while Electronic parts only one side, is this a Double-sided board or a single onel? The answer is obvious. This kind of board is a Double-sided board, it's just install a component on the Double-sided board.
Differences Between Single sided PCB and Double sided PCB

Single and double sided printed circuit boards share the same material make-up: FR-4, which is a form of fiberglass mixed with epoxy. In modern manufacturing, this is usually layered with copper for conductivity and then coated in solder mask for a professional finish. Sometimes, in a process called silk screening, industrial printers print markings and labels on the board as well.
Single-sided PCBs consist of the FR4 insulating core substrate and a thin layer of copper coating on the bottom or solder-side of the substrate. Through-hole components mount on the top or component-side of the substrate with the leads passing through to the bottom side and soldered to the copper pads and tracks. Surface mount components mount directly to the solder side. The primary difference between the two boards will be in conductor placement.
Double-sided boards rely on the same core substrate but have conductors on both sides of the substrate. Very simply, a double-sided board delivers twice the area for conductors. Complex routing can occur with through-hole components mounted on the top layer and surface mount components mounted on the bottom layer. Plated through holes establish [vias" or the electrical connections between the two sides.
Choose Single Sided PCB or Double Sided PCB?
Which PCB you pick depends on your needs and requirements. Sometimes single sided PCBs are more suitable for project design as compared to double sided PCBs and vice versa.
Before you pick any type of PCB for your project, you must take one thing into consideration that single sided PCB layouts are more difficult to route as compared to double sided PCB, but following are the reasons why you should put an effort for making and picking single sided PCB over other PCBs.
Relationship Resources
Multilayer Metal Core PCB
Single Layer Metal Core PCB
Single Sided Flexible PCB