Single Arm Elevator Links ,Drilling Elevator Link,Drilling Elevator Links,Api Elevator Links JIANGSU PETROLEUM MACHINERY CO.,LTD , https://www.jspmgroup.com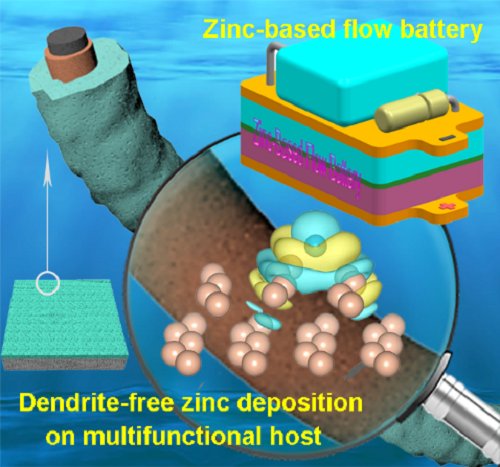
[ Instrument Network Instrument R & D ] Recently, the team of Li Xianfeng and Zhang Huamin, researchers of the Energy Storage Technology Research Department (DNL17) of the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, have proposed a method for sputtering metal on 3D porous carbon felt electrodes using magnetron sputtering technology. The tin layer strategy has achieved the induction of zinc deposition morphology in aqueous zinc-based batteries, effectively reduced the electrochemical deposition overpotential of zinc, eased the growth of zinc dendrites, and made the coulomb efficiency and cycle life of zinc-based batteries obvious improvement.
Coulombic efficiency, also known as discharge efficiency, refers to the ratio of battery discharge capacity to charge capacity during the same cycle, that is, the percentage of discharge capacity to charge capacity. For the positive electrode material, it is the lithium insertion capacity / delithium capacity, that is, the discharge capacity / charge capacity; for the negative electrode material, it is the lithium removal capacity / lithium insertion capacity, that is, the charge capacity / discharge capacity.
Zinc is a chemical element. Its chemical symbol is Zn. Its atomic number is 30. It is located in the fourth periodic table and group IIB in the periodic table of chemical elements. Zinc is a light gray transition metal and the fourth "common" metal. In the modern industry, zinc is an irreplaceable battery and is a very important metal. In addition, zinc is also one of the essential trace elements in the human body and plays an extremely important role.
Zinc negative electrode has the characteristics of low intrinsic electrode potential, fast kinetics, good cycling, and abundant reserves. In zinc-bromine, zinc-iodine, zinc-cerium, zinc-iron flow batteries, zinc-nickel batteries, zinc- The fields of air batteries and zinc ion batteries have attracted widespread attention from researchers. However, the uneven deposition of zinc leads to the growth of dendrites. The dendrites will pierce the separator and cause electrolyte interpenetration, which will reduce the battery coulomb efficiency. At the same time, it will cause a short circuit of the battery, leading to rapid degradation of battery performance. In addition, the abnormal growth of zinc causes zinc Falling off not only reduces the Coulomb efficiency of the battery, but also causes the electrolyte circulation flow path to be blocked and affects the uniformity of the flow field distribution, thereby shortening the cycle life of the battery.
There are many benefits to using an electrolyte as the cathode. The first is that the contact area between the liquid and the medium is large, which helps to increase the capacitance. The second is electrolytic capacitors made of electrolyte, which can withstand high temperatures, so that wave soldering (wave soldering is an important process for SMT chip installation), and the voltage resistance is also strong.
In addition, electrolytic capacitors using an electrolyte as the cathode can self-heal when the dielectric is broken down as long as the breakdown current does not continue. But the electrolyte also has its shortcomings. The first is that it is easy to volatilize and leak under high temperature environment, which has a great impact on life and stability. At high temperature and pressure, the electrolyte may vaporize instantly and increase in volume to cause an explosion (which is often referred to as blasting slurry); the second is The ionic conductivity method used in the electrolyte has a low conductivity, only 0.01S (conductivity, inverse of ohms) / CM, which causes the capacitor's ESR value (equivalent series resistance) to be particularly high.
To this end, the research team selected low-cost metal tin as the morphology-inducing material for electrochemical deposition of zinc, and used magnetron sputtering technology to enable tin to be firmly deposited on a carbon felt negative electrode with a 3D structure without a binder. , Effectively reduce the zinc deposition overpotential and ease the growth of zinc dendrites. Compared with the base material, no matter the zinc-zinc symmetrical flow battery or the zinc-bromine single flow battery, its cycle stability and coulomb efficiency are significantly improved. In addition, the research team used ultra-depth microscopy to characterize the zinc deposition process in situ, combined with theoretical calculations, to briefly analyze the causes of zinc deposition induction. This work provides new ideas for the research of zinc anodes and other metal anodes.