
The Internet of Things data contains four elements: data collection, delivery, processing, and application. The data collection and transmission are basic links. In other words, the future industry chain of the Internet of Things will surely be a "data-driven" industry. In other words, the huge data generated by the connection of objects is processed and processed intelligently to form the final product or service to meet the realm of unmanned service. These applications are the core business value of the Internet of Things.
Giant card Internet of Things
In 1999, researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in the United States raised the concept of the Internet of Things, I am afraid that did not anticipate that its tentacles can now reach every corner of the world. The Internet of Things, a large network that incorporates numerous objects into the online world, has greatly expanded the range of human perception and control capabilities. The latest data from the Pew Research Center shows that in 2025, Internet of Things technology will be ubiquitous, and you will find it difficult to find devices without Internet connectivity, even if it is the most common kettle.
In the past two years, the IoT alliance led by the giants have been established and the open communication platform has been used as a spur to attract more supporters to consolidate the market influence. Apple has hired heavyweight chip makers such as Marvell, Broadcom and Texas Instruments to establish the Home Kit platform and build a smart home market together. Intel created the Open Internet Alliance and joined the Industrial Internet of Things organization. AllSeen Alliance members cover multiple areas, achieve interoperability through the use of open source software and collaborative development, and ultimately realize the vision of “Internet of Everythingâ€. IBM, Cisco, GE, and AT&T have joined forces to form the Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC), which is dedicated to the development of a generic blueprint that enables devices from various vendors to share and transfer data.
Global Internet of Things Strategy
Since 2009, the United States, the European Union, Japan, South Korea and China have all launched their own IoT-related development strategies.
US: After Obama took office as President of the United States, IBM CEO Peng Mingsheng first proposed the concept of “Smart Earth,†and proposed that the new government invest in a new generation of smart infrastructure to clarify its short-term and long-term benefits. Smart Earth, also known as Smart Earth, embeds and equips sensors into power grids, railways, bridges, tunnels, highways, buildings, water systems, dams, oil and gas pipelines, and other objects, and is universally connected to form so-called "intelligence." "Internet of Things," then integrate the "Internet of Things" with the existing Internet to achieve the integration of human society and physical systems.
EU: The European Union has officially established the Internet of Things as a strategic development plan for European ICT. In 2008, the European Internet of Things Conference developed a roadmap for the European Internet of Things policy. In 2009, the European Commission formally issued a number of authoritative documents, in particular the "EU Internet of Things Action Plan."
Japan: Japan On June 14, 2013, Japan passed the Cabinet Meeting Japan's Future IT Strategy “Building the World's Most Advanced IT National Declarationâ€. The declaration puts forward that “20% of Japan’s important infrastructure and aging of sensors will be used before 2020 "Infrastructure testing and maintenance", "Development verification and commercialization of sensor technology and robotics technologies for medical care and life-saving services," and other goals. After Japan announced the "New Strategy for Robots" on January 23 this year, the first conference was held in mid-July on the "IoT Upgrade and Manufacturing Model Working Group." The objective of this working group is to track the development trend of global manufacturing. Science and technology intelligence, through the concerted efforts of the government and private enterprises, realizes the transformation of the Internet of Things technology in the Japanese manufacturing industry.
CNC Milling
In general, computer numerical control milling machine (CNC) machining is a deductive manufacturing technique that programs 3-axis linkage, complex to 5-axis linkage, drives milling cutters to remove layers from solid blocks called blanks to produce finished parts. CNC milling is one of the main types of CNC Machining, which uses cutting tools that rotate at a speed of several thousand to tens of thousands of revolutions per minute (RPM) to precisely remove materials to obtain parts with complex surfaces. In addition to milling, CNC machining is also equipped with drills, boring tools, thread cutters and other tools to complete different part features at once. CNC machining produces parts based on a computer-aided design (CAD) model that is sent to a CNC machine through computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software.
CNC Machining centers developed from CNC milling machines. The biggest difference compare to CNC milling machines is that the machining center has the ability to automatically exchange machining tools, by installing tools for different purposes on the tool magazine, the machining tools on the spindle can be changed through the automatic tool changing device in a single clamping device to achieve a variety of machining functions.
|
CNC Milling Finish
|
|
|
Process
|
Roughness Ra(um)
|
|
Cylindrical milling cutter milling (rough)
|
12.5~3.2
|
|
Cylindrical milling cutter (fine)
|
3.2~0.8
|
|
Cylindrical milling cutter (precision)
|
0.8~0.4
|
|
Cylindrical milling cutter (rough)
|
12.5~3.2
|
|
Cylindrical milling cutter milling (fine)
|
3.2~0.8
|
|
Cylindrical milling cutter milling (precision)
|
0.8~0.4
|
|
Cutter milling (fine)
|
12.5~3.2
|
|
End milling cutter (rough)
|
3.2~0.4
|
|
End milling cutter (precision)
|
0.8~0.2
|
|
High speed milling (rough)
|
1.6~0.8
|
|
High speed milling (fine)
|
0.4~0.2
|
CNC milling accuracy
CNC milling centers and high-Precision Machining centers. Ordinary machining center, resolution of 1μm, maximum feed speed of 15 ~ 25m / min, positioning accuracy of about 0μm. High-precision machining center, resolution of 0.1μm, maximum feed speed of 15 ~ 100m / min, positioning accuracy of about 2μm. Between 2 and 10 μm, with a ± 5 μm more, can be called precision grade. FCE equipped with different grade and different size CNC milling center. Take in to account into both economic and quality in parallel.
CNC Finishing surface treatment
Post-processing is the final step in the CNC machining process. In a quick guide, we offer a lot of surface treatments to complete your final parts and get them to meet strict specific requirements. It should be noted that in CNC machining, post-processing is in optional, as the quality of the machined parts is already very high.
Anodized
The anodizing process allows the part to obtain excellent corrosion resistance, increasing the hardness and wear resistance of the surface. Anodizing is also the most common pre-painting treatment, which can help the painted surface to obtain good adhesion. We typically apply two types of anodizing in our production: Type II, corrosion resistant; Type III is thicker, adding a layer of wear resistance. Both anodizing processes can achieve a variety of color effects.
Polishing
Grinding polish, it offers the fastest turnaround parts and does not require post-processing. The surface finish of the grinding part is equivalent to 125 um in Ra, and the requirements can be increased to 63, 32 or 16 um Ra. Minor tool marks may still be visible on the last part.
Powder coatings
Powder Coating is thermoplastic powder spraying directly on the processed part. The sprayed parts are then baked in an oven to form a durable, abrasion- and corrosion-resistant plastic coating. In the powder coating process, its color, brightness, surface roughness can be customized.
Shot blasting
Shot peening is the high-speed spraying of beads of different hardnesses and sizes onto the surface of the part. To get different textures and brightness of the surface. Since the surface has been hit by similar forging beads, the hardness and wear resistance of the surface have also been enhanced.
Design of CNC machining
CNC machining is a universal machining process, especially parts that can be cut and machined can be achieved through CNC, from simple shape shapes to complex curved structures. However, as with every manufacturing technique, CNC machining has some design limitations. We break them down as follows to ensure that your products are optimally designed to better fit the CNC machining process.
General Tolerance
When designing parts, the size of each part is different according to the application environment, working conditions, etc., and the requirements for the machining accuracy of the workpiece are also different. Although CNC machining can achieve very high machining accuracy, we should also be aware that demanding machining accuracy and accuracy (strict product tolerances) usually mean Longer production times and higher costs. If a specific tolerance is not specified in the product design, we recommend choosing at the following levels.
|
Permissible deviations in mm for ranges in nominal lengths
|
Tolerance Class Designation(Description)
|
|
fine
|
medium
|
coarse
|
very coarse
|
|
0.5 up to 3
|
±0.05
|
±0.1
|
±0.2
|
--
|
|
over 3 up to 6
|
±0.05
|
±0.1
|
±0.3
|
±0.5
|
|
over 6 up to 30
|
±0.1
|
±0.2
|
±0.5
|
±1.0
|
|
over30up to 120
|
±0.15
|
±0.3
|
±0.8
|
±1.5
|
|
over120upto400
|
±0.2
|
±0.5
|
±1.2
|
±2.5
|
|
over 400up to 1000
|
±0.3
|
±0.8
|
±2.0
|
±4.0
|
|
over 1000up to 2000
|
±0.5
|
±1.2
|
±3.0
|
±6.0
|
|
over 2000 up to 4000
|
--
|
±2.0
|
±4.0
|
±8.0
|
The highest precision of our equipment is 0.001, and the recommended most precise machining requirements do not exceed +/-0.005mm
Interior angle
All internal vertical edges of our products need to have rounded corners instead of right angles. This is because the tools used in CNC milling are cylindrical, which means they cannot produce inner right-angled edges. The fillet required by this process is called the inner corner fillet. When designing parts, the larger the inner corner fillet, the more efficient the production process. Because of the larger fillets, larger diameter milling cutters can be used to increase milling speed, and fewer swaps can be made to improve accuracy.
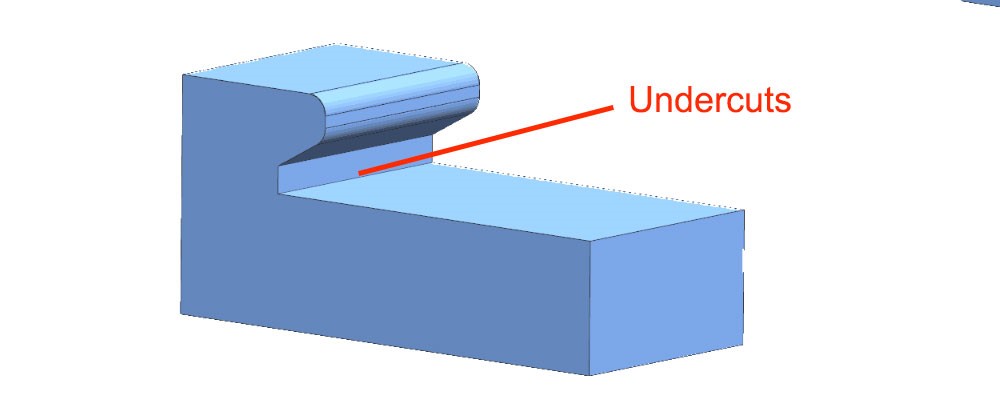
Undercut
Undercut cannot be machined with standard milling cutters, so the use of retract slots for parts should be avoided when designing CNC machined parts. In particular, for non-standard inner contour shapes, customized machining tools are required, which will greatly increase processing time and costs. Secondly, if undercut can not be avoided, due to the limited length of cnc tools, the undercut can not be too deep. If they are too deep or the location is difficult to reach, they will not be able to be produced because the CNC tool cannot reach the machining location.
Chamber wall thickness
CNC machining requires your part design to meet minimum wall thickness requirements. In general, it is recommended to choose the thickest possible and avoid very thin or characteristic walls. This is because CNC tools processing thin-walled parts will cause vibration deformation, which may cause interruptions or damage, and the size is out of specification. The standard minimum wall thickness for CNC machined metals is 0.030" (0.76 mm) and for plastics is 0.060" (1.5 mm).
Thread
When designing parts, it is useful to choose the largest possible thread size because smaller taps have a higher risk of breaking during production. If possible, avoid using deep hole threads as they lead to higher production costs, especially when custom tools are required.
Metal
In principle, materials with high hardness are easier to process because better processing accuracy can be obtained, but they are limited by the hardness of processing tools, so the hardness of the generally recommended parts is 8 ~ 60HRC, and for metal materials, the hardness is greater than stainless steel Followed by cast iron, followed by copper, and finally aluminum, while the processing of ceramics, plastics, etc. belongs to the processing of non-metallic materials. Fast production time.
Polymer
Although CNC can process thermoplastics, the material properties of polymers still have many difficulties for CNC processing. First, due to poor thermal conductivity, many thermoplastics melt or bend when in contact with CNC milling machines or drill bits. Secondly, the processing of plastics, because the hardness is low, the size accuracy caused by the knife during product clamping and processing is not high. For those parts that do not have special requirements for the strength and hardness of the metal, thermoplastics can provide a cheaper alternative.
Cost optimization of machined products
Simplify product design
Simplifying product design while taking into account functionality usually saves production time and reduces production costs. Because the manufacture of complex structures and surfaces often requires complex longer passes, more layering to obtain the same fine contour quality. This means higher production costs.
Reduce cutter changes
Using the same milling machine machining features, larger and same internal fillets, can reduce the number of tools used to reduce machining time. For example, if a workpiece needs a 10mm end face milling cutter to process some features, it also needs a spherical milling cutter to process a curved surface, and a 2mm milling cutter to process a fine groove, which will require repeated tool changes and reduce the machining efficiency
Proper material selection
The choice of raw material for machining can have a significant impact on production time and costs for CNC machining. If possible, choose a material with good processability, such as brass or aluminum. For those applications that do not require metal hardness and strength, CNC machining of engineering plastics like PMMA and ABS also helps to reduce costs because the material blank is cheaper, and the processing efficiency is higher.
Tolerance and wall thickness
Higher tolerances and thinner wall thicknesses also increase THE CORRESPONDING CNC machining costs, as it takes time to achieve higher precision cutting. If your product or component can accept a larger size range, choose a lower tolerance to reduce production time and costs. The same is true for wall thickness: a larger wall thickness margin should be chosen.
Choice of surface treatment
Surface treatment is often the final stage of the CNC machining process, which can also affect the cost of your entire project. Choosing less surface treatment for your part or product can lead to better time and cost efficiency. FCE can recommend to you how to optimize the surface treatment to balance the conflict between cost and quality according to your final needs.
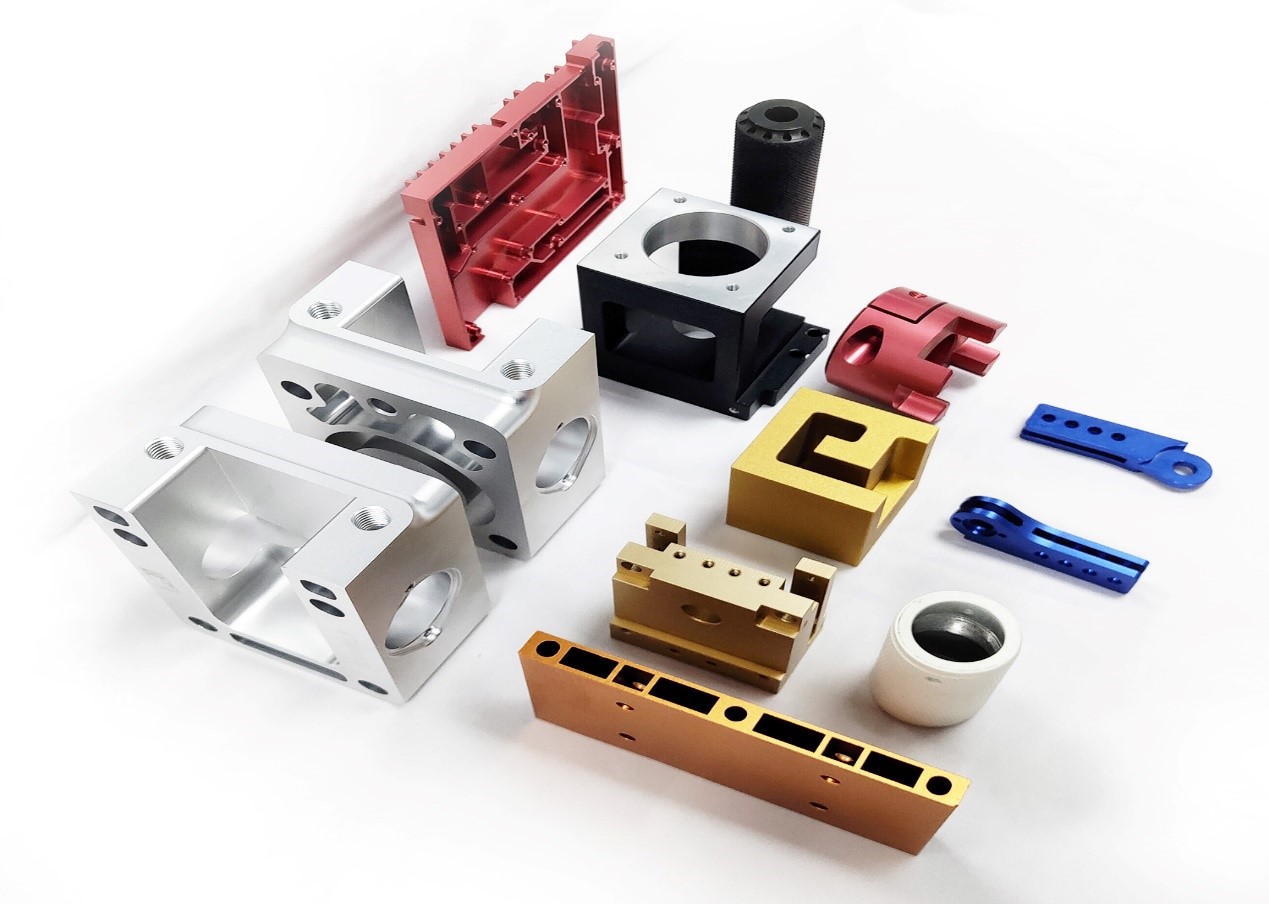
FCE Machining services
FCE facilities are equipped with the most advanced and highest precision 3, 4 and 5-axis CNC machines, which allows us to complete your order in record time
1. 15+ year work experience engineers
2. Fastest 5 days delivery
3. Prototypes can be machined as quickly as 1 day.
4. More than 200 metals and plastics material available in stock
5. Tolerances as low as +-0.005mm
6. ISO 9001: 2015 certified factory
7. 40+ CNC machines
8. 50,000+ machined parts per month
We cooperated with many world top 500 companies and awarded good responds always.



Cnc Milling,Cnc Milling Services,Custom Cnc Milling,Cnc Lathe And Milling Machining
Suzhou FCE precision electronics Co., LTD , https://www.sjfukeyifcesz.com




