Luoyang Golden Egret Geotools Co., Ltd , https://www.hvofpowders.com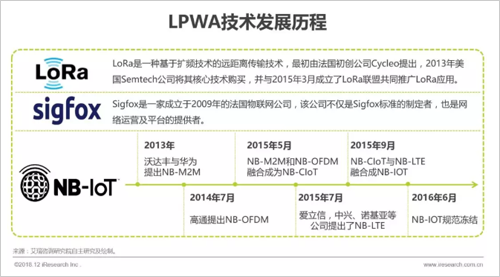
China's LPWAN market has formed two major technology camps, NB-IOT and LoRa. Since its introduction, NB-IOT has been favored by the country and operators. The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology has clearly requested that the base station scale should reach 1.5 million by 2020, and the number of connections should exceed 600 million. The three major operators have actively deployed the NB-IOT network since 2017, and have basically achieved national coverage and are still under construction. Due to the "Technical Requirements for Micropower Short-range Radio Transmission Equipment" (Draft for Comment) issued by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology in December 2017, LoRa's domestic development in the first half of 2018 has been controversial, but with the radio and television, the tower and the Internet giant Tencent, Ali has joined the LoRa camp, which undoubtedly injects a "cardiotonic agent" for LoRa's domestic development. What is the future development of the two technologies in China?
NB-IOT (Narrow Band Internet of Things) and LoRa (long range) are the main development of the Internet of Things LPWA technology in China. Factors such as national policies, working frequency bands, technical characteristics, network environment and application scenarios will affect the development of the two technologies in China. However, in the future, NB-IOT will be the mainstay to promote the common development of LPWAN. For solution providers and application enterprises, when deploying the network, select the appropriate wireless communication technology based on the network environment and the scenario requirements.
NB-IOT is an international standard and LoRa is a proprietary technology.
LPWA technology is designed for low-speed, low-power, wide-coverage and large-connected IoT applications. The current mainstream LPWA technologies are NB-IOT, eMTC, LoRa and sigfox. The NB-IOT is developed by the 3GPP, a very authoritative standardization organization in the communications industry, and is approved by the International Telecommunication Union ITU. It belongs to the international standard; LoRa's core technology is in the hands of Semtech in the United States and belongs to the private technology of the enterprise.
NB-IOT and LoRa battle
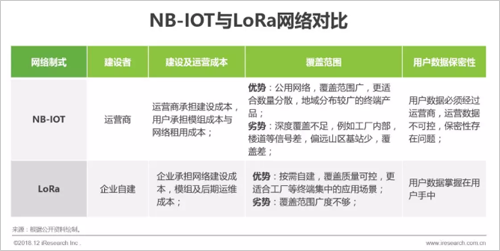
1. NB-IOT working frequency band can provide higher service quality by national allocation
The radio spectrum, that is, radio waves, is an electromagnetic wave between 3HZ and 30GHZ. It is a limited non-renewable resource. Governments all over the world have classified the spectrum as state-owned, regulated and paid for.
The NB-IOT frequency bands used by the three major domestic operators are uniformly allocated by the state, and there is no risk of being cleared. A relatively clean wireless environment provides a higher quality of service. The 470-518MHz used by LoRa in China is the frequency band allocated to the broadcasting and television by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology. The "Technical Requirements for Micropower Short-range Radio Transmission Equipment" (Draft for Comment) issued in December 2017 stipulates that this frequency band can be used for radio meter reading. However, there are restrictions on the transmission power, frequency, etc., and if the interference to the local broadcasting service is to be discontinued, the formal use of this requirement will have a fatal blow to LoRa development. At present, the industry promotes LoRa technology in cooperation with local radio and television. However, after all, it does not meet the requirements of the radio regulatory agency. If the country redistributes the frequency band, there is a risk of being cleaned up. The wireless environment is complex, the interference is large, and the communication quality cannot be guaranteed.
2. NB-IOT is more suitable for high-speed and frequent communication applications than LoRa.
The NB-IOT and LoRa design concepts differ from the way in which they are transmitted, resulting in differences in communication capabilities. LoRa is designed for low power consumption. It adopts asynchronous transmission mode. The terminal does not need to synchronize with the base station in real time to reduce the power consumption of the terminal. However, each communication needs to carry the synchronization signal, thus increasing the frequency resource overhead and resulting in low frequency utilization. NB-IOT is a 4G-based cellular communication technology. The original design concept is Zui's excellent frequency utilization to increase the transmission rate. Synchronous transmission is adopted. Communication does not need to carry synchronization signals to reduce frequency overhead and improve spectrum utilization. However, it is necessary to maintain synchronization with the base station in real time to increase the power consumption of the terminal. Because NB-IOT has higher spectrum utilization rate, it can provide higher transmission rate than LoRa. The theoretical value of NB-IOT uplink peak speed is 5 times that of LoRa.
When the communication is not required, the terminal enters the sleep state to reduce the power consumption. The base station can only issue the command when the terminal wakes up, causing the downlink delay to be high. To meet the communication frequency requirements of different scenarios, LoRaWAN defines ClassA, ClassB, and ClassC. In the three terminal working modes, the sleep period is successively decreased, and the power consumption is sequentially increased. The NB-IOT specifies three working modes of PSM, eDRX and DRX. The functions are similar to the three terminal working modes of LoRa, and the power consumption is reduced by hibernation, but In terms of performance, NB-IOT can provide smaller downlink delay, which is more suitable for frequent communication applications than LoRa.
3. NB-IOT belongs to the carrier network, and LoRa can be deployed on demand.
Limited by network operation licenses and business licenses, only operators are qualified to build and operate an NB-IOT network nationwide. Currently, no company in China has the qualifications and capabilities to build a LoRa WAN network and operate in the country. A private LoRa network can be deployed on a small scale without an application, and a government license is required for scale deployment. Therefore, the NB-IOT belongs to the carrier network and can realize contiguous coverage, and is more suitable for a distributed application scenario in which the terminal area is widely distributed and has mobility. For industrial applications where the terminal is stationary and concentrated, both NB-IOT and LoRa can meet the needs, and should be selected based on the network environment and individual needs.
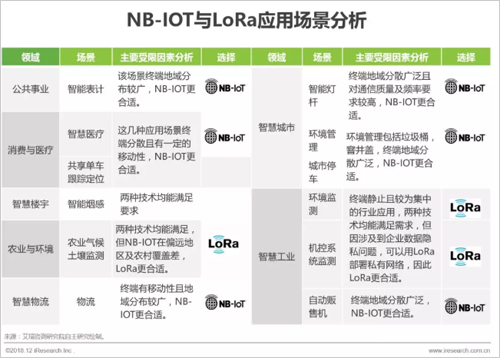
4, NB-IOT and LoRa application scenario analysis
According to the application field, the application scenarios of LPWA technology can be subdivided into seven vertical markets: public utilities, consumer and medical, smart industry, smart buildings, agriculture and environment, smart logistics and smart city. Because different IoT scenarios have different requirements for wireless communication technologies, it is necessary to select a suitable communication technology based on the network environment and specific scenario requirements when deploying the network.
NB-IOT is supplemented by LoRa and promotes the development of LPWAN
The Internet of Everything will bring tens of billions of connections. LPWA technology is mainly used in the seven vertical areas as the main force of the wide-area Internet of Things. The application scenarios are highly differentiated and the industry features are obvious. A single technology cannot meet all the scene requirements. The two technologies must find their respective positions between the competition and the competition, and finally show the situation that NB-IOT is the main synergistic development of LoRa. At present, the two technologies are the same in the domestically focused industry, and the application scenarios have been overlapped. The promoters of the two technologies should focus on the firepower to expand more application scenarios based on the technical characteristics, and truly open the application space of the LPWA technology.