First, the importance of engineering drawings in the machinery industry At present, the domestic mechanical design basically takes the 2D engineering drawing as the final design result. If you use 2D > CAD, you don't need to say much more. It's a drawing directly. With 3D > CAD, only the 3D model is obviously not enough: a) Manufacturing and processing. According to the current situation in China, it is obviously impossible to complete drawing without drawings. As long as it is not NC machining, it is bound to have engineering drawings. The 3D model can be used as an effective aid, but it is impossible to process parts only by virtue of the 3D model. b) Inspection. Similarly, the inspection is also inseparable from the two-dimensional drawings, the inspection data including the dimensions, tolerances, shape tolerances, roughness and other expressions on the two-dimensional drawings more clearly; c) Assembly. The three-dimensional model can intuitively show the state of the assembly, but the two-dimensional engineering drawing has its special advantages in terms of expressing the internal structure, representing the assembly relationship, some special instructions, and generating detailed lists. d) Archiving. After the product design is completed, to ensure the frozen state of the product, the three-dimensional model is dependent on software, and the software is always changing during the upgrade, so the product status is difficult to control, the product version control is also very easy to make mistakes, 2D drawings will not There are these concerns. v) Data exchange. If the two parties to the exchange use different software, the conversion loss of two-dimensional data is much less than that of three-dimensional data. From this we can see that 2D engineering drawings play a very important role in practical applications. The strength of three-dimensional modules has greatly accelerated our design speed and greatly improved design quality, but the final output still depends on two-dimensional engineering drawings. Although the three-dimensional function of three-dimensional software is stronger, the better, but in the actual design, the proportion of particularly complex parts is small, while the engineering drawing is every assembly must be out of each assembly, so that the engineering drawing The powerful software of the module is really useful software. >2 Formulation of standards There can be multiple sets of standards in the system standard. The standardization department can define multiple sets of standards to be placed here, and the designer can select the appropriate standard drawing. There can only be one current standard, which means that a drawing can only have one standard. There are two sets of default system standards in the software: >GB and >ISO (changes can be deleted). Because the contents of the standard regulations are very wide, and various companies in various industries have different understandings of the standards because of their own characteristics, these two standards can only serve as a reference. We begin to create a new standard, first select the system standard option from the drop-down list, the standardized work should be carried out under the system standard. l New standard "Right-click → New" on the "standard" root node will generate an empty standard. The empty standard has only one name and does not contain any styles. Right-clicking on the existing standard name will use the selected standard as The template generates a copy standard. The copy standard is exactly the same as the original standard. Based on this, a small number of changes can be made to generate a new standard. Right-click on a new standard on >GB and change the name to "Enterprise Standard". Right click on "Enterprise Standard" to activate it. After activation, the standard name font is bold and the default current standard when creating a new drawing is the activation standard in the system standard. After activation, it facilitates subsequent editing of the standard. l Define the standard Click on the company logo, the icon content appears on the right display area: The style type is the style category name, which corresponds to the tree list on the left. Take "Size" as an example. The list on the left lists all the style names included in the size. The right display area lists more detailed contents: The check mark before the name indicates that the style belongs to the currently selected standard ( That is, “Enterprise Standardâ€), the style can be selected or selected by clicking on the standard; the “Default†in the comment indicates that the style is the default style of this standard. A standard can contain multiple size styles, but the default style of size can only be one, the default style can not be selected, you can set other styles as default (right name → default) Select again. Select “Enterprise Standard†and click on the “General†tab in the display area to set some basic parameters of the standard: line width series value and text height series value. After setting, under this standard, setting the line width and setting the font style can only be selected from this series to achieve the standardization effect. "Enterprise Standard" is a copy of ">GB" when it was newly created, which is exactly the same as ">GB". In general, the standard line width series values ​​and text height series values ​​based on the national standard are the same, so a slight change here can meet the requirements; if you start a new empty standard, the series of values ​​here is a One added. Define the style Style is the most basic thing of a multi-standard system. Standards are composed of styles. The difference between different standards is actually the difference of style combinations. Ø Take the arrow style as an example: In >10 style categories, fonts and arrows are two special categories. In addition to being applied directly to drawings, these two types of styles are also referenced by other styles. Therefore, these two types of styles should be used as much as possible for engineering drawings and other styles. Since the "Enterprise Standard" was generated as a copy of ">GB", the styles in both standards are the same. The "dot (>GB)", "benchmark (>GB)", "arrow (>GB)", and "none" >4 styles are both ">GB" and "enterprise standard" (observe carefully, we can find In fact, the "None" pattern still belongs to ">ISO"). According to need, select the style that does not conform to “Enterprise Standard†or select it into another suitable style (click “Enterprise Standard†→ select the arrow in the available style in the display area → click the box in front of the style name). You can right-click the root of the "Arrow" or right-click the "Arrow (>GB)" style name to create a new style. Select "Add to activation criteria", the new style is added to the "enterprise standard"; otherwise it just adds a style in the system, but does not belong to any one standard. Change the "copy arrow (>GB)" to "arrow (enterprise)". The style name should be as simple and accurate as possible to reflect the attributes and characteristics of the style. After setting, set parameters such as shape, length and aspect ratio of the arrow and save. If the content of the display area is modified, the system will prompt whether to save it if it is not saved and switch to another page; if the “Save Tip†option of the lower left corner of the interface is checked off, the page will not be prompted and saved automatically when the page is switched. Ø Then define the size style: Create a new dimension style named "General (Enterprise Standard)". There are many attributes of size, so it is divided into three pages: text, display, and tolerance. Under the “Display†page, you can select the “Arrow (Company)†you have just set in the drop-down list of the arrow style, set the length of the end line, the length of the drawn line, and set the expression of the radius and diameter. Ø The same method defines other styles. l output standard After all the styles are defined, click on the standard name, select or select a style in the display area, and set the default style. Finally, right click on the “Enterprise Standard†→ Output and export the entire standard to a file called “Enterprise Standardâ€. The standard can be used by designers for input. l Some explanations Ø If a style is referenced by multiple standards, after changing the specific content of the style, all standards will change accordingly, so try to avoid repeated references to the style; Ø Styles can refer to font styles and arrow styles that are not in the standard, but styles that are not in the standard are lost when the standard is output. Ø A single style can also be output as a file. Through the above process, the standardization department has already completed a standard and the design department can use it to produce a map. l input standard Create a new drawing file. The popup dialog box can select the standard to use. The default is the system activation standard. At this time, the design department system standard only comes with>GB and >ISO, and the default is >GB. Start the "Standard Manager" and switch to the system standard. Click the [Enter] button to import the "Enterprise Standard" file that you created above. The standard is set as the activation standard, then the newly created drawing defaults to this standard. l current standard Start Standard Manager and the default location is Current Standard. The initial state of the current standard is the same as the system standard of the same name. It is saved along with the file to avoid data loss when the file is opened without the same system standard. Changes to the current standard content do not affect system settings. Click on the root node of the tree list to see if a style is referenced by the standard, the current standard or style is consistent with the system standard or style of the same name. Right-click updates will keep the current system consistent. The standard change is normal. When the standard changes, drawings that have already been generated before the multi-standard system is changed are very troublesome. You need to find out where the new standard is not met, and then modify them one by one. After the style is adopted, the standard update only requires one operation under the standard manager. Or take the size as an example. If the generated drawing font has the text type> 5, the arrow is solid, the length is> 4mm, and the aspect ratio> 4: >1 style='font-family: Song'>, the length of the endline is >3mm, while the new standard specifies the font to be Arial>3.5, the arrow is hollow, length>5mm, aspect ratio>4: >1 style='font-family: Song'>, and the length of the endline is >1mm. We have two methods to change, method one: the system standard re-enter the new standard, and then update the current; method two: the current standard is modified according to the new standard. After the standard manager is closed, the dimensions of all dependent styles on the drawing have been updated to the new standard. l Switching standard For the current file, you can click [Switch Criteria] to switch the current standard to another standard. Existing label styles can choose whether to change to the new standard's default style. As a result, the conversion of different standard drawings has also become easier. l Switch style With the multi-standard system, each default label object is styled. Each label object edit is more convenient than the previous version. Click the layer style toolbar > The list shows all the available styles for this type of object in the current file. The horizontal line shows the style that the current standard belongs to, and the horizontal line shows the style that is not the current standard. The object can still modify an attribute individually. After the attribute is modified, the attribute remains unchanged when the style in the standard is changed; but when the object is switched to another style and then switched back, the attribute follows the style. Still taking the size as an example. If the size is style >1: the arrow is solid and the length is longer than 4mm, the arrow in the attribute will be hollow and >3.5mm long. If the arrow in style >1 is changed to >1mm, The dot, which still belongs to style >1, but the arrow remains hollow >3.5mm; if you switch the dimension to another style and switch back to style >1, the arrow of that dimension becomes a dot >1mm in diameter, and The style is the same. l Some explanations Ø After the old version file is opened, the system activation standard is the default. Existing labels have no style. Ø style support format brush Now that we have a general understanding of the process of using the Solid3000 V7.0 multi-standard system, we can see from the above introduction that the multi-standard system brings the following benefits to the design drawing: >1 Facilitates the implementation of standardization work. Greatly improve the efficiency of the map, reduce the conflict between the standardization department and the design department, and reduce the workload of both parties. >2 facilitates cooperation between working groups. Even if different people have different drawing habits, the unified standards and styles will be unified after the collection, and the drawings will be uniform. >3 facilitates drawing changes. Whether it is a standard update or a switching standard, you don't need to look for it in the diagram. You only need to set it up in the standard manager. >4 Facilitate the exchange of resources. Different companies have different standards. When drawings are exchanged (such as external processing, external design, etc.), simply change the standard manager to achieve the “business habit†of the drawings. In short, with the multi-standard system, Solid3000 makes the management of drawings between multiple departments or other companies more efficient and simple, and designers can put more energy into the design. Fermentation Tank,Unitank Fermenter,Fermentation Vessel,Large Fermentation Vessel Wenzhou Zoncic Machinery Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.zoncicmachinery.com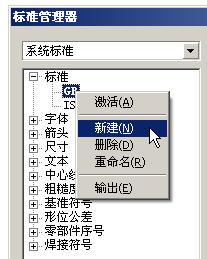





 Buttons can switch objects from one style to another.
Buttons can switch objects from one style to another. 